![]() LC 1206. 设计跳表
(opens new window) (opens new window)
LC 1206. 设计跳表
(opens new window) (opens new window)
困难
# 问题描述
不使用任何库函数,设计一个 跳表 。
跳表 是在 O(log(n)) 时间内完成增加、删除、搜索操作的数据结构。跳表相比于树堆与红黑树,其功能与性能相当,并且跳表的代码长度相较下更短,其设计思想与链表相似。
例如,一个跳表包含 [30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 90] ,然后增加 80、45 到跳表中,以下图的方式操作:
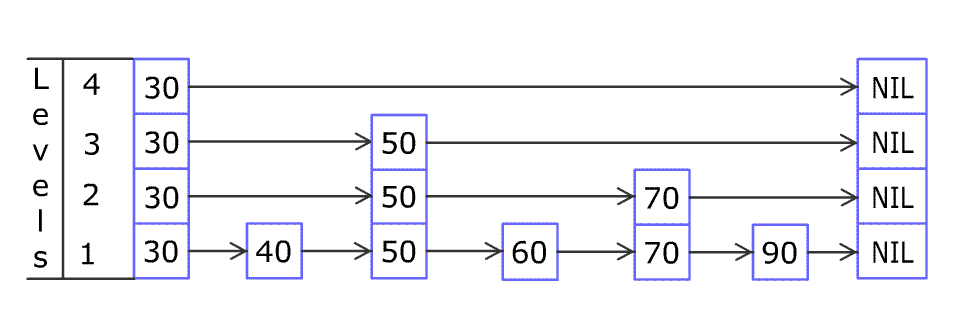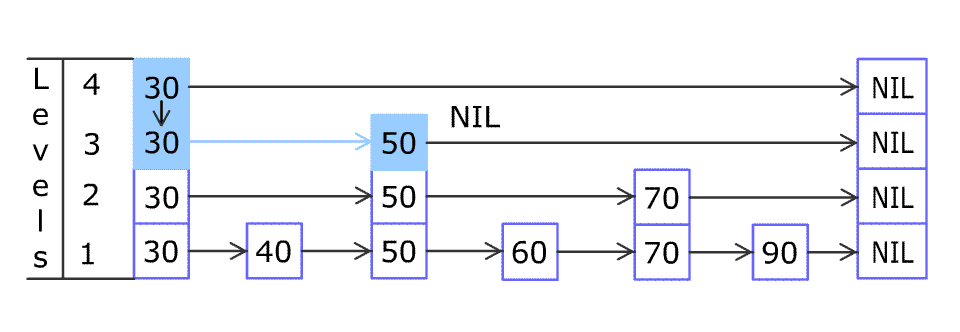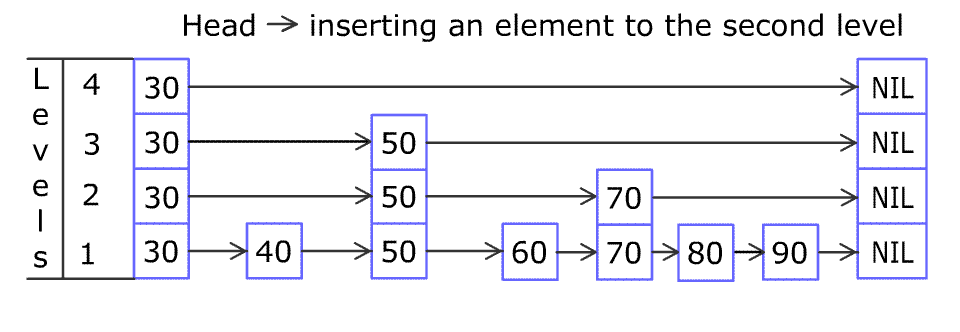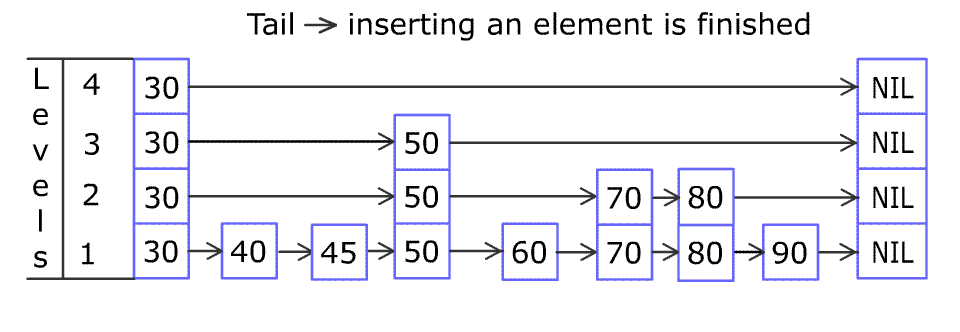
Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons (opens new window)
跳表中有很多层,每一层是一个短的链表。在第一层的作用下,增加、删除和搜索操作的时间复杂度不超过 O(n)。跳表的每一个操作的平均时间复杂度是 O(log(n)),空间复杂度是 O(n)。
了解更多 : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list (opens new window)
在本题中,你的设计应该要包含这些函数:
bool search(int target): 返回 target 是否存在于跳表中。void add(int num): 插入一个元素到跳表。bool erase(int num): 在跳表中删除一个值,如果num不存在,直接返回false. 如果存在多个num,删除其中任意一个即可。
注意,跳表中可能存在多个相同的值,你的代码需要处理这种情况。
示例 1:
输入
["Skiplist", "add", "add", "add", "search", "add", "search", "erase", "erase", "search"]
[[], [1], [2], [3], [0], [4], [1], [0], [1], [1]]
输出
[null, null, null, null, false, null, true, false, true, false]
解释
Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist();
skiplist.add(1);
skiplist.add(2);
skiplist.add(3);
skiplist.search(0); // 返回 false
skiplist.add(4);
skiplist.search(1); // 返回 true
skiplist.erase(0); // 返回 false,0 不在跳表中
skiplist.erase(1); // 返回 true
skiplist.search(1); // 返回 false,1 已被擦除
提示:
0 <= num, target <= 2 * 104- 调用
search,add,erase操作次数不大于5 * 104
# 直接构造
此题是跳表原理的实现,跳表原理可以参考官方题解 (opens new window)
var MAX_LEVEL = 8
class SkiplistNode {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val
this.next = new Array(MAX_LEVEL)
}
}
var Skiplist = function () {
this.head = new SkiplistNode(-1)
}
/**
* @param {number} target
* @return {Array}
*/
Skiplist.prototype.find = function (target) {
const node = new Array(MAX_LEVEL)
let curr = this.head
for (let i = MAX_LEVEL - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (curr.next[i] && curr.next[i].val < target) curr = curr.next[i]
node[i] = curr
}
return node
}
/**
* @param {number} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
Skiplist.prototype.search = function (target) {
const nodes = this.find(target)
return nodes[0].next[0] != null && nodes[0].next[0].val === target
}
/**
* @param {number} num
* @return {void}
*/
Skiplist.prototype.add = function (num) {
const nodes = this.find(num)
const node = new SkiplistNode(num)
for (let i = 0; i < MAX_LEVEL; i++) {
node.next[i] = nodes[i].next[i]
nodes[i].next[i] = node
if (Math.round(Math.random())) break
}
}
/**
* @param {number} num
* @return {boolean}
*/
Skiplist.prototype.erase = function (num) {
const nodes = this.find(num)
if (!nodes[0].next[0] || nodes[0].next[0].val !== num) return false
for (let i = 0; i < MAX_LEVEL; i++) {
if (nodes[i].next[i]) nodes[i].next[i] = nodes[i].next[i].next[i]
}
return true
}
/**
* Your Skiplist object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new Skiplist()
* var param_1 = obj.search(target)
* obj.add(num)
* var param_3 = obj.erase(num)
*/
- 时间复杂度:
- 空间复杂度:
上次更新: 2023/01/31 19:48:05
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 , 转载请注明出处!